By: Terry Cyfers, Business Coach
 So, you have an idea for a business—now what do you do?
So, you have an idea for a business—now what do you do?
Write a business plan, of course. But most people’s idea of a business plan is a 40+ page document, and the dread of undertaking such a daunting task scares them away from fulfilling their dreams. Yet without a business plan, you can’t clear your path to success.
Overwhelmed? Relax. There’s no need to write a book. A business plan is simply a written document that sets the direction of the business.
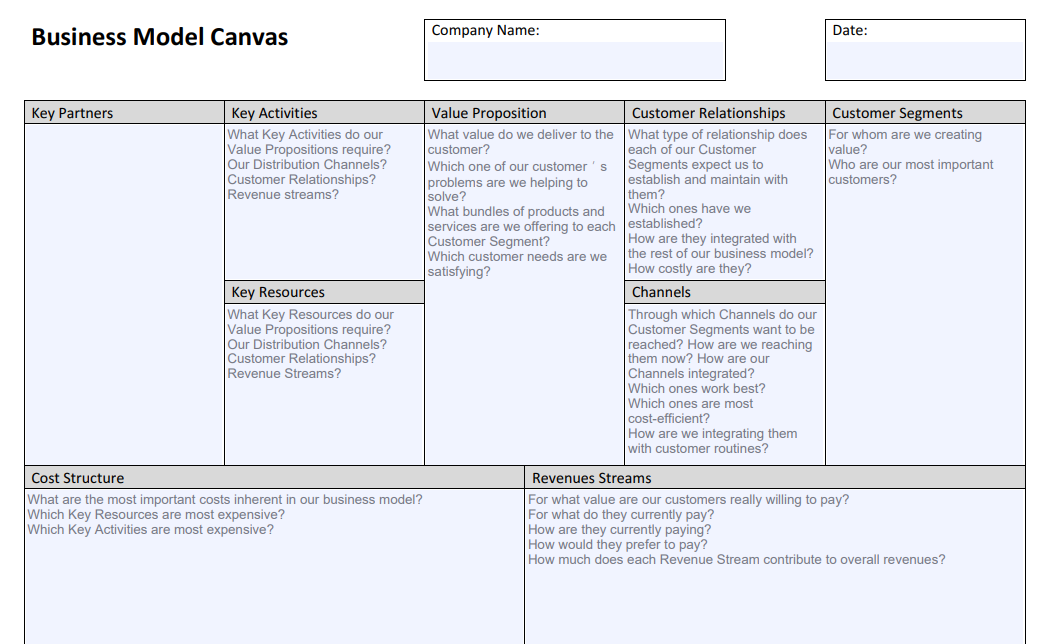
The Business Model Canvas uses nine blocks to help you set the direction of your new business. The blocks represent the most critical areas of focus for an entrepreneur wanting to start, expand or diversify a business. These are the business considerations that provide a forward impulse to a business within its marketplace.
The Business Model Canvas was invented by Alexander Osterwalder, a Swiss entrepreneur, business theorist and consultant. Osterwalder has written and co-authored several books, including “Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, And Challengers.”
This template provides you with a blank canvas on which to create your masterpiece. Let’s start by filling in the middle box, then move from right to left.

Block 1—Key Partners
Who are my key partners? Who are my suppliers? Who are my allies that contribute to the functioning of my business? Key partners can help reduce the risk and uncertainty.
Block 2—Key Activities
What activities are needed to reach the intended markets and generate revenue? Are these activities:
- Production/Manufacturing?
- Problem Solving?
- Platform/Network?
How are you delivering the activities? Remember, each customer segment or product/service needs its own set of activities.
Block 3—Key Resources
What key resources will you need for your product or service? What type of assets will be needed to permit the business to create and deliver on these products and services? What will you need to reach the intended markets and customer segments, and maintain those relationships in order to generate revenue? Remember, these assets can be:
- Physical/fixed
- Financial
- Intellectual property
- Human capital
- Be owned, leased or in partnership
Block 4—Value Proposition
Why are you starting your business? How does your product or service fill the void in your market area? What value do you deliver to your customer? What problems are you hoping to solve? How does your product and services alleviate the customer’s problem? Your value proposition should be measurable by both quality and quantity.
Block 5—Customer Relationships
What type of relationship does each customer expect you to establish and maintain? Do they expect human interaction? Do they want self-service? Do they want someone dedicated to meet their needs?
Block 6—Channels
How are you going to communicate with the customer? What channels of communication, distribution or sales are the means that establish this contact? The main function is to:
- Make the customers aware of your products and services
- Assist the clients in evaluating these products and services
- Align the customers with specific products or services
Block 7—Customer Segments
To whom are you selling your product or service? You are seeking clients that can take advantage of your product or service by gaining something or relieving a problem. Who are the groups of people or organizations your company hopes to reach and serve that have common needs and behaviors? Your demographics might include multiple customer archetypes.
Block 8— Cost Structure
What are the costs incurred to deliver the product or service? What are the most important costs for your business model? What are your most expensive resources? What are your most expensive activities? Are your costs fixed or variable? Fixed costs do not change as a function of volume or services provided. Some examples include rent or utilities. Variable costs vary in direct proportion to the volume of the product or services produced.
By using this method, the answered questions allow you to form a clear picture of the direction for your new venture.
Block 9—Revenue Streams
How much is the customer willing to pay for this valued product or service? How will they pay for these services?
Types of revenue streams include:
- Transactional: Payments that are made only once per transaction
- Recurring Transactions: Periodic payments in exchange for product or service to continue after the original transaction
What will be the pricing strategy?
- Fixed: Based on predefined prices
- Dynamic: Based on market conditions
